Thermal Vapor Recompression - TVR
Home
- / GIG Karasek Portfolio Overview
- / Thermal Vapor Recompression - TVR
Reduction of live steam and cooling water through steam-based evaporation
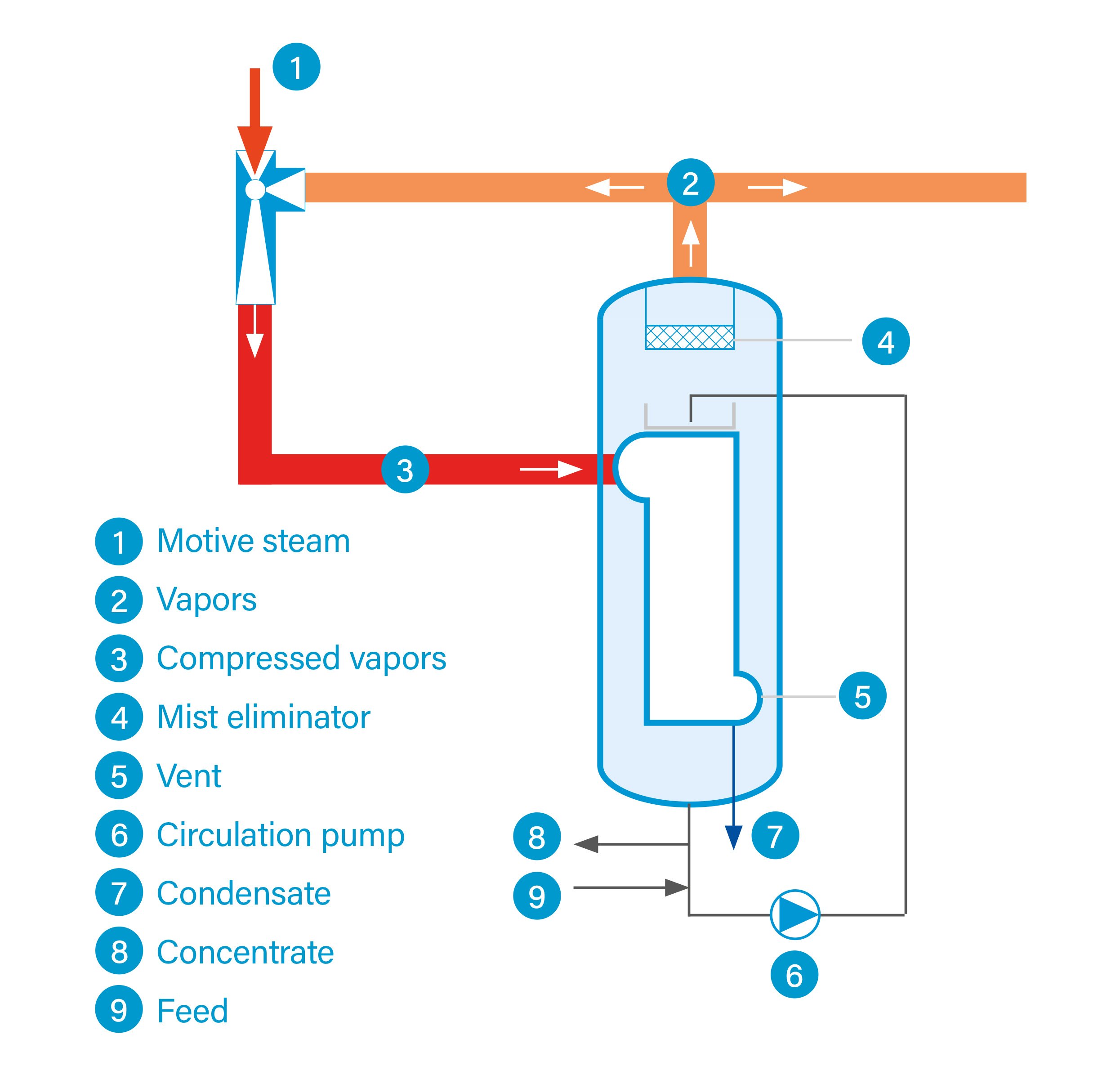
Thermal vapor recompression (TVR) is based on the same principle as the mechanical alternative (MVR) but uses only a portion of the generated vapor for heating the system. Steam is used as the energy source.
@ GIG Karasek
Functional principle
Thermal vapor recompression uses part of the process vapor to heat the evaporator. The other part is passed on to the next stage or converted into condensate.
Steam compression for heat recovery takes place in a steam jet compressor, which is usually designed for a specific operating point. Motive steam (live steam) is required to operate a thermal vapor recompressor.
Typical operating parameters
-
Dimensions: 300 – 10.000 sqm
-
Feed rates: 5.000 kg/h – 150.000 kg/h
-
Operating pressure: ≥ 80 mbar abs.
-
Heating temperature: ≤ 200°C
-
Operating pressure: -1 / +5 bar(g)
-
Viscosity: ≤ 250 mPas
Preconditions
-
The main product is water or water with a negligible content of organic substances.
-
The distillate can be easily evaporated to supply vapor for the ejectors.
-
The heating medium is available at the required temperature level.
-
Moderate difference between upper and lower temperature.

Visit our Newsroom!
Here you can find the latest NEWS, our EVENT CALENDAR or further INSIGHTS featuring our key topics.





